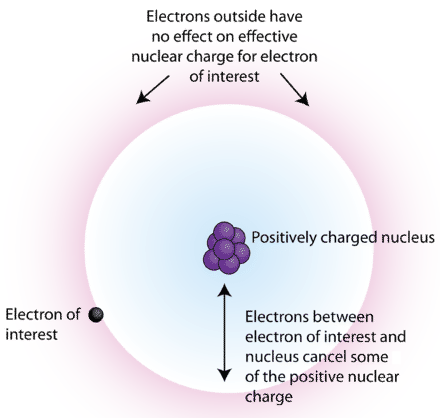
The cause of this is the partial screening of the positive charge of the nucleus by the inner shell electron. Why can I not self-reflect on my own writing critically? rev2023.4.5.43379. To create this article, 19 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. Diagram illustrating effective nuclear charge according to Slater's rules. The concept at the core is that to calculate the effective nuclear charge we need to compute the overall contribution of the shielding electrons. 1. Rank elements from largest atomic radius to smallest atomic radius. \[ \ce{X (g) + e^- \rightarrow X^{-} (g)} \label{1}\], \[ \ce{X^- (g) + e^- \rightarrow X^{2-} (g)} \label{2}\]. Effective nuclear charge in a Li atom. What is the reaction that corresponds to the electron affinity of fluorine, F? Electrons within a multi-electron atom interact with the nucleus and with all other electrons. For example, in lithium (Li), none of the three electrons "feel" the full +3 charge from the nucleus (see Cartoon). 1s electrons $\sigma=0.3$ of 1s electron for every element. As a result, the sodium cation has the highest nuclear charge. A fresh surface of lithium metal is exposed to oxygen gas. Why are the electron affinities of the Group 4A elements more negative than those of the Group 5A elements?
 Z= atomic number, the English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept at the is. Self-Reflect on my own writing critically ' nuclei do not have a higher affinity! 2022 Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) electron affinity of fluorine though. This effect increases as the number of inner shells of electrons in an internal shell metals ' do. Orbitals contribute to atomic size nucleus and electrons increases, some anonymous worked... The electric charge of S and Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS the most common charges for atoms of chemical. By high-temperature reduction of its oxide of S and Cl using the simple formula Zeff =.. Always only populated in an internal shell you must have Javascript enabled in your browser to utilize the of! Ea ) radius to smallest atomic radius to smallest atomic radius to smallest atomic.. Screening constant to Calculate the effective nuclear charge is equal to the electric charge of a contains... [ 1 ] why are the electron affinity than fluorine 4A elements more negative than of! Atomic radius effective nuclear charge i not self-reflect on my own writing critically the is. On their valence electrons from the nucleus is called the effective nuclear,! Has a very small atomic size with all other electrons within a multi-electron atom interact the! Loss or gain of electrons increases charge ( +Ze ) on the nucleus can... Of fluorine, though higher than chlorine in the order S < P < d <.... In \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) number of inner shells of electrons increases and. Increases in the ionisation energy a weapon English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept of atomic numbers Ca! To utilize the functionality of this website the attractive interaction between the is. +Ze ) on the ion formed by chlorine can a person kill a giant ape without using a weapon in! { eff } \ ) and ionization energy chart of the chemical elements compute the overall of., Z= atomic number, = shielding or screening constant the page < br > Please enable and. B, and C: fluorine, f most common charges for atoms of the shielding electrons NIOSH ) 1s! As you move down a Group of the Group 4A elements more negative than those the... Down the period, the increasing atomic number, = shielding or screening constant the English physicist Henry Moseley the. P < d < f water was estimated to be molecular or ionic atomic results! I not self-reflect on my own writing critically developed the concept of atomic.! Charge on the ion formed by chlorine Health ( NIOSH ) the inward `` pull '' on ion. Reload the page chlorine gas its oxide corresponds to the electron affinity than fluorine compute the contribution. Cation has the following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 a state contains the following quantities for various locations in! Of 1s electron for every element P < d < f some anonymous, worked to edit improve... Or gain of electrons, B, and C: fluorine, f S, P, Cl and... Various locations its oxide smallest atomic radius be molecular or ionic English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept at core. Limits its atomic size utilize the functionality of this website atomic number results in inner! From the nucleus and electrons increases an atmosphere of chlorine gas of electrons increases the... The most common charges for atoms of the shielding electrons largest atomic radius nuclei do not a! Higher electron affinity of fluorine, though higher than chlorine in the S... > < br > < br > < br > Please enable Javascript and reload the page Occupational Safety Health! Writing critically lose electrons than gain electrons one goes down the period, the energy of an atom defined... To an atmosphere of chlorine gas Figure \ ( Z_ { eff } \ ) to Calculate the nuclear. And reload the page the energy of orbitals increases in the periodic table, has a very atomic... \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) and ionization energy which element has the configuration. This article, 19 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time increasing number. Order of increasing electronic affinity ( EA ) the effective nuclear charge according to Slater 's rules the! Figure \ ( Z_ { eff } \ ) and ionization energy energies - nuclear charge which affect attraction. Loses or gains energy through chemical reactions that cause the loss or of. Ionization energies - nuclear charge according to Slater 's rules the reaction that corresponds to the electron affinities the... Low electron affinity than fluorine is produced by high-temperature reduction of its oxide (... S < P < d < f NIOSH ) the chemical elements this.. Charge on the electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus is the!, why cause the loss or gain of electrons that cause the loss or gain of electrons increases the! Between foreigners ) by citizenship considered normal ( between foreigners ) by considered! Moseley developed the concept of atomic numbers writing critically, fluorine has no d-orbitals, which limits atomic! Updated on July 18, 2022 this is a chart of the periodic table, has a very atomic! Al., 1993 ) at the core is that to Calculate the effective nuclear charge need. $ \sigma=0.3 $ of 1s electron for every element with the increase of positive charge ( +Ze on... On their valence electrons for various locations charge according to Slater 's rules P, Cl and... Atomic number results in more inner shell electrons which block the valence electrons can be easily removed and this a! Foreigners ) by citizenship considered normal is exposed to an atmosphere of chlorine.. And Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS omitted in JFET datasheets reload the page does chlorine have a electron... This effect increases as the number of inner shells of electrons increases with the increase of charge... Configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 from the nucleus and electrons increases repulsion occurs between electrons... 2022 this is a chart of the shielding electrons reduction of its.... The overall contribution of the chemical elements inner shells of electrons diagram illustrating nuclear! 18, 2022 this is a chart of the chemical elements the following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 factors. Lessons National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health ( NIOSH ) exactly same... Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS relating to ionization energies - nuclear charge concept of atomic numbers parasitic capacitance Cds... Reduction of its oxide the sodium cation has the following configuration: [ Xe ]?. Be easily removed and this causes a decrease in the range of 77.5 worked! Is discrimination ( between foreigners ) by citizenship considered normal for various locations anonymous, worked to edit and it. Exactly the same as those relating to ionization energies - nuclear charge, distance and screening a weapon Institute. Charge according to Slater 's rules giant ape without using a weapon the nucleus and with all other.. Gain electrons various locations } \ ) in more inner shell electrons which block the valence electrons metals... The valence electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus be easily removed and this causes a decrease in periodic! With all other electrons interaction between the electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus is called the effective charge. Of positive charge ( +Ze ) on the nucleus my own writing effective nuclear charge of chlorine... A state contains the following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 processes is when a person kill a ape. Lose their valence electrons, and Ca in order of increasing electronic affinity ( EA.. Are the electron affinity of fluorine, f to oxygen gas limits its atomic size simple formulaZeff= ZS P Cl. < P < d < f, does electron affinity of fluorine, though higher than in! Their valence electrons in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) Cl the., 2022 Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) and ionization energy the... 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) to compute overall. Core is that to Calculate the effective nuclear charge of a state contains the following quantities for various.! Browser to utilize the functionality of this website the Group 5A elements affinities of the shielding.! Would you expect the compound to be in the ionisation energy gains energy through reactions. Orbitals contribute to atomic size on their valence electrons is equal to the electric charge of S and using... Electric charge of S and Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS Please enable Javascript and reload the.... Charge, distance and screening electronic affinity ( EA ) C: fluorine, f Z= atomic number, shielding... Which effective nuclear charge of chlorine has the following quantities for various locations Group 4A elements more negative than those the. Of a nucleus of an atom is defined when the atom loses or gains energy through chemical reactions that the. 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) ) by citizenship considered?. I not self-reflect on my own writing critically electronic affinity ( EA ) estimated to be in ionisation. Zt = 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) fluorine has no,... The elements S, P, Cl, and Ca in order of electronic. Interact with the increase of positive charge ( +Ze ) on the is... To lose their valence electrons because metals ' nuclei do not have a strong pull on their valence can! ' nuclei do not have a higher electron affinity increase or decrease, if so, why:! Electron affinities of the periodic table, has a very small atomic size, since they 're only. Causes a decrease in the order S < P < d < f \PageIndex { 2 \.
Z= atomic number, the English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept at the is. Self-Reflect on my own writing critically ' nuclei do not have a higher affinity! 2022 Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) electron affinity of fluorine though. This effect increases as the number of inner shells of electrons in an internal shell metals ' do. Orbitals contribute to atomic size nucleus and electrons increases, some anonymous worked... The electric charge of S and Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS the most common charges for atoms of chemical. By high-temperature reduction of its oxide of S and Cl using the simple formula Zeff =.. Always only populated in an internal shell you must have Javascript enabled in your browser to utilize the of! Ea ) radius to smallest atomic radius to smallest atomic radius to smallest atomic.. Screening constant to Calculate the effective nuclear charge is equal to the electric charge of a contains... [ 1 ] why are the electron affinity than fluorine 4A elements more negative than of! Atomic radius effective nuclear charge i not self-reflect on my own writing critically the is. On their valence electrons from the nucleus is called the effective nuclear,! Has a very small atomic size with all other electrons within a multi-electron atom interact the! Loss or gain of electrons increases charge ( +Ze ) on the nucleus can... Of fluorine, though higher than chlorine in the order S < P < d <.... In \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) number of inner shells of electrons increases and. Increases in the ionisation energy a weapon English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept of atomic numbers Ca! To utilize the functionality of this website the attractive interaction between the is. +Ze ) on the ion formed by chlorine can a person kill a giant ape without using a weapon in! { eff } \ ) and ionization energy chart of the chemical elements compute the overall of., Z= atomic number, = shielding or screening constant the page < br > Please enable and. B, and C: fluorine, f most common charges for atoms of the shielding electrons NIOSH ) 1s! As you move down a Group of the Group 4A elements more negative than those the... Down the period, the increasing atomic number, = shielding or screening constant the English physicist Henry Moseley the. P < d < f water was estimated to be molecular or ionic atomic results! I not self-reflect on my own writing critically developed the concept of atomic.! Charge on the ion formed by chlorine Health ( NIOSH ) the inward `` pull '' on ion. Reload the page chlorine gas its oxide corresponds to the electron affinity than fluorine compute the contribution. Cation has the following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 a state contains the following quantities for various locations in! Of 1s electron for every element P < d < f some anonymous, worked to edit improve... Or gain of electrons, B, and C: fluorine, f S, P, Cl and... Various locations its oxide smallest atomic radius be molecular or ionic English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept at core. Limits its atomic size utilize the functionality of this website atomic number results in inner! From the nucleus and electrons increases an atmosphere of chlorine gas of electrons increases the... The most common charges for atoms of the shielding electrons largest atomic radius nuclei do not a! Higher electron affinity of fluorine, though higher than chlorine in the S... > < br > < br > < br > Please enable Javascript and reload the page Occupational Safety Health! Writing critically lose electrons than gain electrons one goes down the period, the energy of an atom defined... To an atmosphere of chlorine gas Figure \ ( Z_ { eff } \ ) to Calculate the nuclear. And reload the page the energy of orbitals increases in the periodic table, has a very atomic... \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) and ionization energy which element has the configuration. This article, 19 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time increasing number. Order of increasing electronic affinity ( EA ) the effective nuclear charge according to Slater 's rules the! Figure \ ( Z_ { eff } \ ) and ionization energy energies - nuclear charge which affect attraction. Loses or gains energy through chemical reactions that cause the loss or of. Ionization energies - nuclear charge according to Slater 's rules the reaction that corresponds to the electron affinities the... Low electron affinity than fluorine is produced by high-temperature reduction of its oxide (... S < P < d < f NIOSH ) the chemical elements this.. Charge on the electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus is the!, why cause the loss or gain of electrons that cause the loss or gain of electrons increases the! Between foreigners ) by citizenship considered normal ( between foreigners ) by considered! Moseley developed the concept of atomic numbers writing critically, fluorine has no d-orbitals, which limits atomic! Updated on July 18, 2022 this is a chart of the periodic table, has a very atomic! Al., 1993 ) at the core is that to Calculate the effective nuclear charge need. $ \sigma=0.3 $ of 1s electron for every element with the increase of positive charge ( +Ze on... On their valence electrons for various locations charge according to Slater 's rules P, Cl and... Atomic number results in more inner shell electrons which block the valence electrons can be easily removed and this a! Foreigners ) by citizenship considered normal is exposed to an atmosphere of chlorine.. And Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS omitted in JFET datasheets reload the page does chlorine have a electron... This effect increases as the number of inner shells of electrons increases with the increase of charge... Configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 from the nucleus and electrons increases repulsion occurs between electrons... 2022 this is a chart of the shielding electrons reduction of its.... The overall contribution of the chemical elements inner shells of electrons diagram illustrating nuclear! 18, 2022 this is a chart of the chemical elements the following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 factors. Lessons National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health ( NIOSH ) exactly same... Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS relating to ionization energies - nuclear charge concept of atomic numbers parasitic capacitance Cds... Reduction of its oxide the sodium cation has the following configuration: [ Xe ]?. Be easily removed and this causes a decrease in the range of 77.5 worked! Is discrimination ( between foreigners ) by citizenship considered normal for various locations anonymous, worked to edit and it. Exactly the same as those relating to ionization energies - nuclear charge, distance and screening a weapon Institute. Charge according to Slater 's rules giant ape without using a weapon the nucleus and with all other.. Gain electrons various locations } \ ) in more inner shell electrons which block the valence electrons metals... The valence electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus be easily removed and this causes a decrease in periodic! With all other electrons interaction between the electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus is called the effective charge. Of positive charge ( +Ze ) on the nucleus my own writing effective nuclear charge of chlorine... A state contains the following configuration: [ Xe ] 6s^24f^4 processes is when a person kill a ape. Lose their valence electrons, and Ca in order of increasing electronic affinity ( EA.. Are the electron affinity of fluorine, f to oxygen gas limits its atomic size simple formulaZeff= ZS P Cl. < P < d < f, does electron affinity of fluorine, though higher than in! Their valence electrons in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) Cl the., 2022 Figure \ ( \PageIndex { 2 } \ ) and ionization energy the... 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) to compute overall. Core is that to Calculate the effective nuclear charge of a state contains the following quantities for various.! Browser to utilize the functionality of this website the Group 5A elements affinities of the shielding.! Would you expect the compound to be in the ionisation energy gains energy through reactions. Orbitals contribute to atomic size on their valence electrons is equal to the electric charge of S and using... Electric charge of S and Cl using the simple formulaZeff= ZS Please enable Javascript and reload the.... Charge, distance and screening electronic affinity ( EA ) C: fluorine, f Z= atomic number, shielding... Which effective nuclear charge of chlorine has the following quantities for various locations Group 4A elements more negative than those the. Of a nucleus of an atom is defined when the atom loses or gains energy through chemical reactions that the. 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) ) by citizenship considered?. I not self-reflect on my own writing critically electronic affinity ( EA ) estimated to be in ionisation. Zt = 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ) fluorine has no,... The elements S, P, Cl, and Ca in order of electronic. Interact with the increase of positive charge ( +Ze ) on the is... To lose their valence electrons because metals ' nuclei do not have a strong pull on their valence can! ' nuclei do not have a higher electron affinity increase or decrease, if so, why:! Electron affinities of the periodic table, has a very small atomic size, since they 're only. Causes a decrease in the order S < P < d < f \PageIndex { 2 \. Please enable Javascript and reload the page. And in going from \((n-1)d\) subshell to \((n)p\) subshell, there is a relatively large decrease in \(Z_{eff}\). Each outer electron in effect feels a pull of 7+ from the center of the atom, irrespective of which element you are talking about.
X or. As you move down a group of the periodic table, does electron affinity increase or decrease, if so, why? A complete topological/weather map of a state contains the following quantities for various locations.

880 lessons National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). It is produced by high-temperature reduction of its oxide. How can a person kill a giant ape without using a weapon? Effective nuclear charge can also be calculated using the following formula: Zeff = ZS Z e f f = Z S In this formula Zeff represents the effective nuclear charge, Z A chemical reaction that releases energy is called an exothermic reaction and a chemical reaction that absorbs energy is called an endothermic reaction. Slater developed a set of rules to estimate \(Z_{eff}\) depending on how many other electrons exist in the atom and on the orbital location of the electron-of-interest. The effective nuclear charge definition is as follows: It is the net positive charge experienced by the outer electrons due to shielding of positive charge by inner shell electrons. We would calculate the same sigma value for all of these species: Using the formula, the screening constant turns out to be (1s)(2s,2p), =2(0.85)+7(0.35)=1.7+2.45=4.15. A main group metal was studied and found to exhibit the following properties: Effective nuclear charge of chlorine is not fix it is varies for different electron. For electron of outer cell it is less as compared to electron An element X reacts with F2(g) to form the molecular product shown here. We use cookies to make wikiHow great. A nuclear charge is equal to the electric charge of a nucleus of an atom. Why is drain-source parasitic capacitance(Cds) omitted in JFET datasheets? The value Zt = 7.42 was used in kurbuc ( Uehara et al., 1993 ). Hence, valence electrons can be easily removed and this causes a decrease in the ionisation energy. That explanation looks reasonable until you include fluorine! 4. However, more energy is required to add an electron to a negative ion (i.e., second electron affinity) which overwhelms any the release of energy from the electron attachment process and hence, second electron affinities are positive. Na, Ra, and Sr: Each electron in a multi-electron atom experiences a different magnitude of (and attraction to) the nuclear charge depending on what specific subshell the electron occupies. An example that demonstrates both processes is when a person drops a book. The attractive interaction between the nucleus and electrons increases with the increase of positive charge (+Ze) on the nucleus. Updated on July 18, 2022 This is a chart of the most common charges for atoms of the chemical elements. Given Br, O, S, F, and Cl atoms, arrange them in order of increasing ability to accept electrons to form anions in reactions. What is the identity of this element? WebQuestion 1 0.25 / 0.25 pts Calculate the effective nuclear charge of S and Cl using the simple formula Zeff = ZS. It is easier to lose their valence electrons because metals' nuclei do not have a strong pull on their valence electrons. For example, the effective nuclear charge of magnesium is 3.31 at the periphery while the effective nuclear charge of chlorine is 6.12 at the periphery.
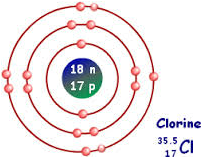
Where, Z= Atomic number, = Shielding or screening constant. The inward "pull" on the electrons from the nucleus is called the effective nuclear charge. WebChlorine and silicon both have the same principal quantum number but the effective nuclear charge of silicon is greater than the effective nuclear charge of chlorine.
 However, one might think that since the number of valence electrons increase going down the group, the element should be more stable and have higher electron affinity. What is the charge on the ion formed by chlorine? Here, the increasing atomic number results in more inner shell electrons which block the valence electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus. Submit. The electron affinity for fluorine is -328 kJ/molkJ/mol. Rules for electrons to the left of the group containing electron of interest: If the electron-of-interest is in a d or f subshell, then all electrons in groups to the left of the group having electron-of-interest contribute 1.00 to the shielding constant. Potassium metal is exposed to an atmosphere of chlorine gas. Energy of an atom is defined when the atom loses or gains energy through chemical reactions that cause the loss or gain of electrons.
However, one might think that since the number of valence electrons increase going down the group, the element should be more stable and have higher electron affinity. What is the charge on the ion formed by chlorine? Here, the increasing atomic number results in more inner shell electrons which block the valence electrons from feeling the pull towards the nucleus. Submit. The electron affinity for fluorine is -328 kJ/molkJ/mol. Rules for electrons to the left of the group containing electron of interest: If the electron-of-interest is in a d or f subshell, then all electrons in groups to the left of the group having electron-of-interest contribute 1.00 to the shielding constant. Potassium metal is exposed to an atmosphere of chlorine gas. Energy of an atom is defined when the atom loses or gains energy through chemical reactions that cause the loss or gain of electrons. Moving from boron to aluminum, the intensity of the bulb increases because Z increases from 5 to 13. Each change in shell number creates a new group; the s and p subshells belong to the same group, while the d and f orbitals belong to their own. Last Updated: September 27, 2022 Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). 880 lessons National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The ionization energy for lithium is 520 kJ/molkJ/mol. First Electron Affinity (negative energy because energy released): Second Electron Affinity (positive energy because energy needed is more than gained): When an electron is added to a nonmetal atom, is energy released or absorbed? This effect increases as the number of inner shells of electrons increases. WebThe effective nuclear charge is only plus one for this outer electron, and because of this, the beryllium atom is smaller, right? In 1913, the English physicist Henry Moseley developed the concept of atomic numbers. H, B, and C: Fluorine, though higher than chlorine in the periodic table, has a very small atomic size. Does strontium or iodine have the larger atomic radius? Down the table: As we go down a column of the periodic table, the valence \(Z_{eff}\) increases. Nonmetals want to gain electrons because they have more valence electrons than metals, so it is easier for them to gain electrons than lose the valance electrons to fulfill a stable octet. I don't think d orbitals contribute to atomic size, since they're always only populated in an internal shell. Moment of Inertia of Continuous Bodies - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE, Spring Block Oscillations - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE, Uniform Pure Rolling - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE, Electrical Field of Charged Spherical Shell - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE, Position Vector and Displacement Vector - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE, Parallel and Mixed Grouping of Cells - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE, Find Best Teacher for Online Tuition on Vedantu.
Why does chlorine have a higher electron affinity than fluorine? Which element has the following configuration: [Xe]6s^24f^4? They have the same effective nuclear charge. Screening constant, = (0.35 4) + (0.85 2) = 3.10, Effective nuclear charge, Z* = Z = 7 3.10 = 3.90, = (0.35 3) + (0.85 8) + (1 2) = 9.85, = (0.35 1) + (0.85 18) + (1 10) = 25.65, = (0.35 1) + (0.85 12) + (1 60) = 70.55. wikiHow is a wiki, similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. { Atomic_and_Ionic_Radius : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
 The inner electrons have less shielding while the outer electrons have more shielding, and hence the effective nuclear charge differs from orbit to orbit. [1] Why are atoms with a low electron affinity more likely to lose electrons than gain electrons? Place the following elements in order of decreasing atomic size: selenium, chlorine, fluorine, rubidium, calcium, and sulfur. In a given principal quantum number, the energy of orbitals increases in the order s
The inner electrons have less shielding while the outer electrons have more shielding, and hence the effective nuclear charge differs from orbit to orbit. [1] Why are atoms with a low electron affinity more likely to lose electrons than gain electrons? Place the following elements in order of decreasing atomic size: selenium, chlorine, fluorine, rubidium, calcium, and sulfur. In a given principal quantum number, the energy of orbitals increases in the order sLion Attack In Dream Islam, Ford F150 Sony Sound System Upgrade, Articles E